Aircraft play a vital role in modern transportation. They connect countries, support trade, and enable rapid travel. Over time, Aircraft overview and design have evolved to improve safety, efficiency, and performance. Understanding how aircraft are designed helps explain how they fly and why they look the way they do.
What Is an Aircraft?
An aircraft is a vehicle designed to fly in the air. It uses aerodynamic forces to stay airborne. While there are many types of aircraft, most share common design principles. These principles focus on balance, lift, thrust, and control. Together, they allow the aircraft to move smoothly through the air.
Aircraft can be grouped into categories such as airplanes, helicopters, and gliders. Each type serves a different purpose. However, the core design elements remain largely the same.
Key Components of Aircraft Design
The fuselage forms the main body of the aircraft. It holds passengers, cargo, and essential systems. Designers shape the fuselage to reduce air resistance. As a result, the aircraft can move faster while using less fuel.
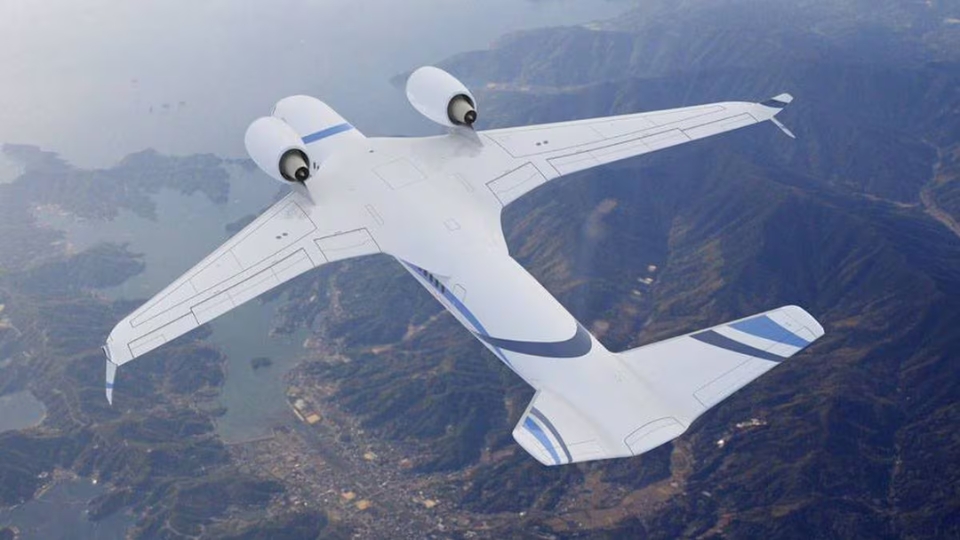
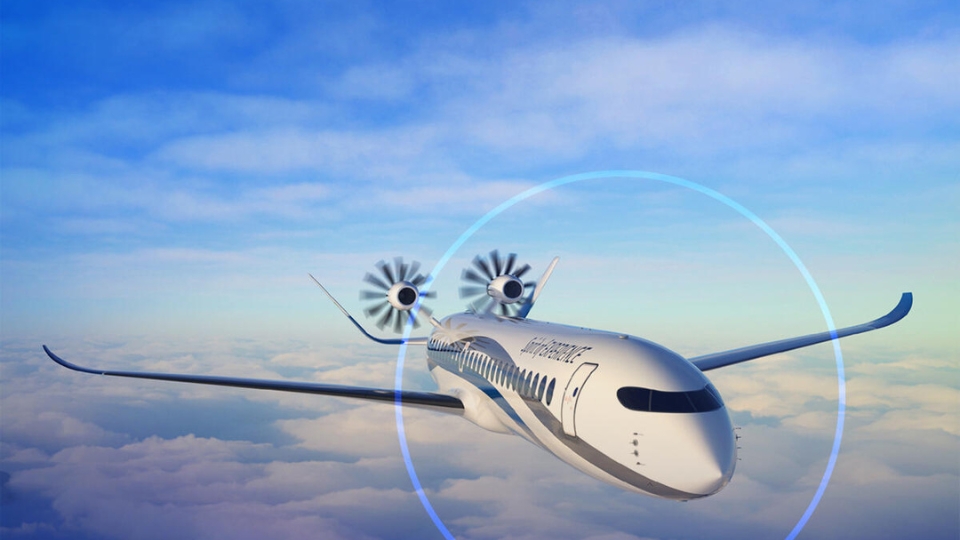
Next are the wings, which are crucial for flight. Wings generate lift when air flows over and under them. Their shape, known as an airfoil, controls how efficiently lift is produced. Longer wings often improve fuel efficiency. Shorter wings, however, can increase speed and agility.
The tail section helps maintain stability. It includes horizontal and vertical stabilizers. These parts keep the aircraft balanced during flight. They also assist the pilot in controlling direction and altitude.
Engines and Propulsion Systems
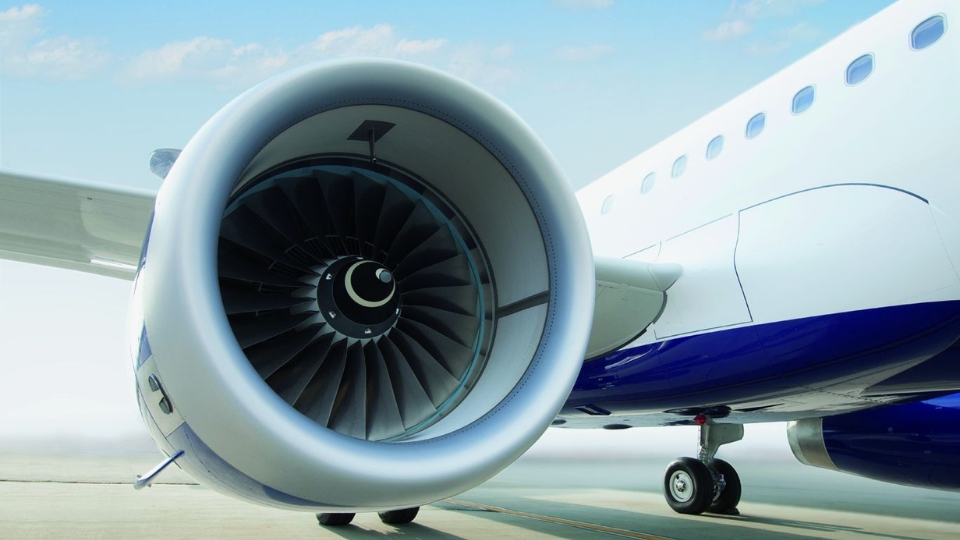
Aircraft need thrust to move forward. This force comes from engines. Smaller aircraft often use piston or turboprop engines. In contrast, commercial jets rely on jet engines. Jet engines provide strong thrust and support long-distance travel.
Engine placement is also important. Some engines are mounted under the wings, while others sit at the rear. Each option has benefits. For example, underwing engines improve balance and ease of maintenance.
Materials Used in Aircraft Construction
Early aircraft used wood and fabric. Today, manufacturers rely on advanced materials. Aluminum remains common due to its strength and light weight. However, modern aircraft increasingly use composite materials.
Composites, such as carbon fiber, reduce weight while increasing durability. As a result, aircraft consume less fuel and produce fewer emissions. This shift supports both performance and environmental goals.
Aerodynamics and Efficiency
Aerodynamics plays a major role in aircraft design. Designers aim to reduce drag, which slows the aircraft down. Smooth surfaces and streamlined shapes help air flow efficiently.
Winglets, found at the tips of wings, are a good example. They reduce air turbulence and improve fuel efficiency. Small design changes like this can lead to significant savings over time.

Aircraft overview and design
Safety and Comfort Considerations
Safety is always a top priority. Designers include multiple backup systems to handle emergencies. These systems ensure continued operation even if one component fails.
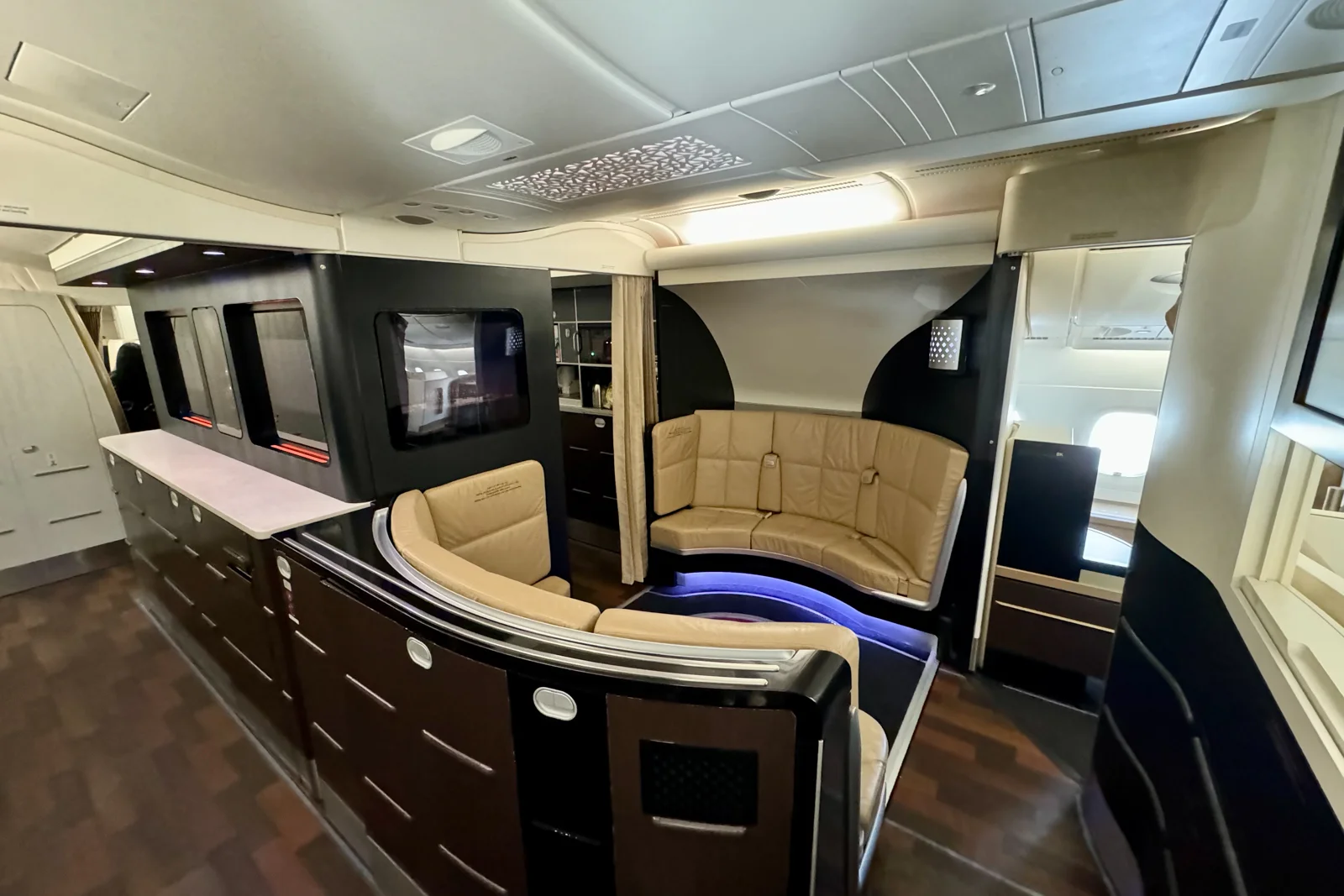
At the same time, passenger comfort matters. Cabin layout, noise reduction, and air pressure control all influence the travel experience. Therefore, modern aircraft balance technical performance with human comfort.
Conclusion
Aircraft design combines science, engineering, and innovation. Every component has a clear purpose. From wings to engines, each part works together to ensure safe and efficient flight. As technology advances, aircraft will continue to become lighter, smarter, and more sustainable.