Fuel efficiency remains one of the top priorities in modern aviation. Airlines constantly seek ways to reduce fuel costs and minimize environmental impact. Aircraft manufacturers respond by designing planes that use less energy without compromising safety or performance. Through aerodynamic shapes, advanced materials, and cutting-edge technology, every new model aims to fly farther using less fuel.
Design improvements not only help airlines save money but also support global sustainability goals. By enhancing efficiency, aircraft can reduce emissions and contribute to cleaner skies.
The Role of Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics plays a vital role in determining how much fuel an aircraft consumes. The smoother a plane moves through the air, the less drag it creates. Reduced drag means less engine thrust is required, which directly saves fuel.
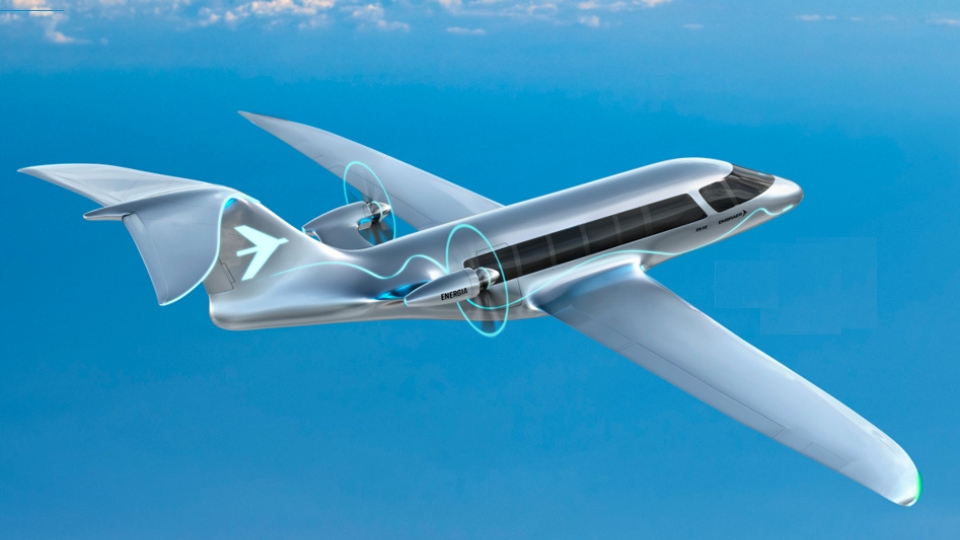
Engineers design aircraft with sleek fuselages and optimized wings to minimize air resistance. Features like winglets—small upward curves at the tips of wings—further improve airflow. They prevent vortices from forming, which reduces drag and enhances lift.
Additionally, modern computer simulations allow engineers to test various wing and body designs before production. This ensures that every curve and angle contributes to efficient flight performance.

How Aircraft Design Improves Fuel Efficiency
Lightweight Materials That Reduce Fuel Burn
Weight has a direct impact on fuel usage. The heavier the aircraft, the more power it needs to stay airborne. To address this, manufacturers use lightweight materials such as carbon-fiber composites, titanium, and advanced aluminum alloys.
Carbon-fiber composites provide exceptional strength while weighing significantly less than traditional metals. These materials are now used for wings, fuselage sections, and interior components. Titanium, although more expensive, offers durability and heat resistance, especially in engine areas.
Moreover, the combination of lighter materials and strong structural integrity improves both performance and safety. Each kilogram saved translates to reduced fuel consumption over thousands of flights, creating long-term savings for airlines.
Maximizing Value During Travel Downtime
The efficiency of a travel schedule includes optimizing the moments of downtime with rewarding and accessible entertainment options that offer great value. For a trusted source of digital leisure that maximizes your return on time, you can find a comprehensive guide to the top payout casinos listed by casinous.com.
Efficient Wing Design
The shape and structure of wings greatly influence an aircraft’s fuel efficiency. Designers focus on creating wings that produce maximum lift with minimal drag. Longer, thinner wings—known as high aspect ratio designs — are now common in modern airliners.
These wings allow aircraft to glide more smoothly, using less energy during cruise. Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner and Airbus’s A350 both use this approach, demonstrating how structural design enhances fuel savings.
Furthermore, movable wingtips and adaptive flaps improve performance in different flight phases. They adjust during takeoff, cruising, and landing to optimize aerodynamic balance. As a result, the plane consumes less fuel throughout the journey.
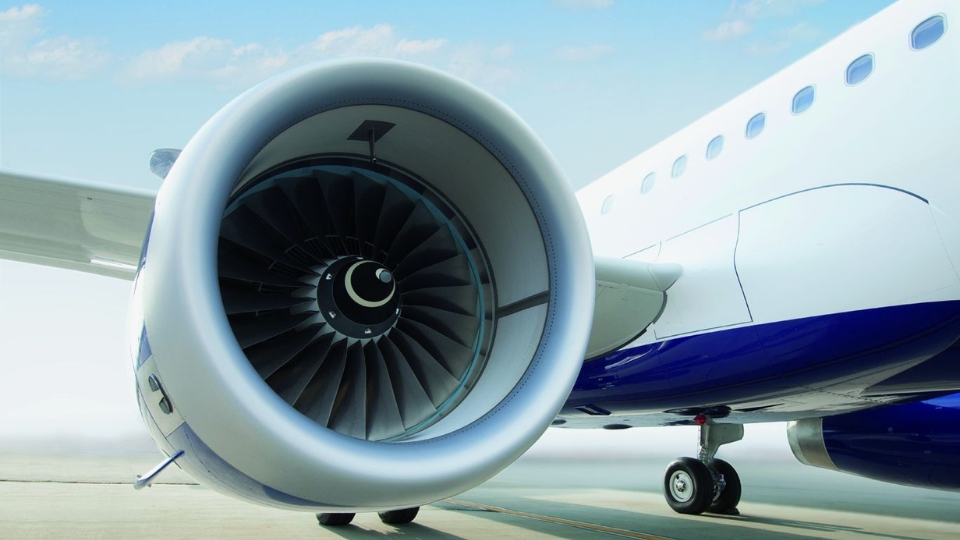
Engine Integration and Placement
Modern aircraft design also focuses on engine placement and integration. Mounting engines under the wings helps reduce drag and improve airflow efficiency. The positioning also balances the aircraft’s center of gravity, which contributes to smoother flight dynamics.
Advanced engine designs complement aerodynamic improvements. New-generation turbofan engines use larger fans that move more air at lower speeds, producing more thrust while using less fuel.
Manufacturers also incorporate noise-reduction features and high-bypass ratios that enhance efficiency and passenger comfort. Together, engine design and placement form a crucial part of fuel-saving innovation.
Smarter Cabin and Interior Design
Fuel efficiency doesn’t depend solely on aerodynamics or engines. Interior design also contributes to overall performance. Airlines and manufacturers collaborate to make cabins lighter without reducing comfort.
Seats, flooring, and storage compartments now use lightweight composite materials. LED lighting systems consume less energy than older models. Even galley equipment is optimized for weight reduction.
In addition, modern layouts maximize passenger capacity while maintaining comfort and balance. Efficient space management ensures optimal weight distribution, which enhances overall flight stability and reduces energy demand.
Advanced Flight Control Systems
Technology plays a major role in improving aircraft performance. Modern flight control systems automatically adjust wing surfaces, engine thrust, and flight paths for optimal efficiency. These systems use real-time data to monitor weather, altitude, and airspeed.
Pilots receive continuous feedback to help maintain the most fuel-efficient trajectory. Digital autopilot systems now optimize cruise altitude and speed, reducing unnecessary fuel burn.
Furthermore, some aircraft use predictive software that suggests smoother routes based on air traffic and wind conditions. This innovation allows flights to save both time and fuel simultaneously.
Sustainable Innovations for the Future
Aviation continues to evolve toward greener solutions. Hybrid-electric engines, hydrogen-powered aircraft, and sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are currently in development. These innovations aim to further reduce fuel dependency while maintaining strong performance.
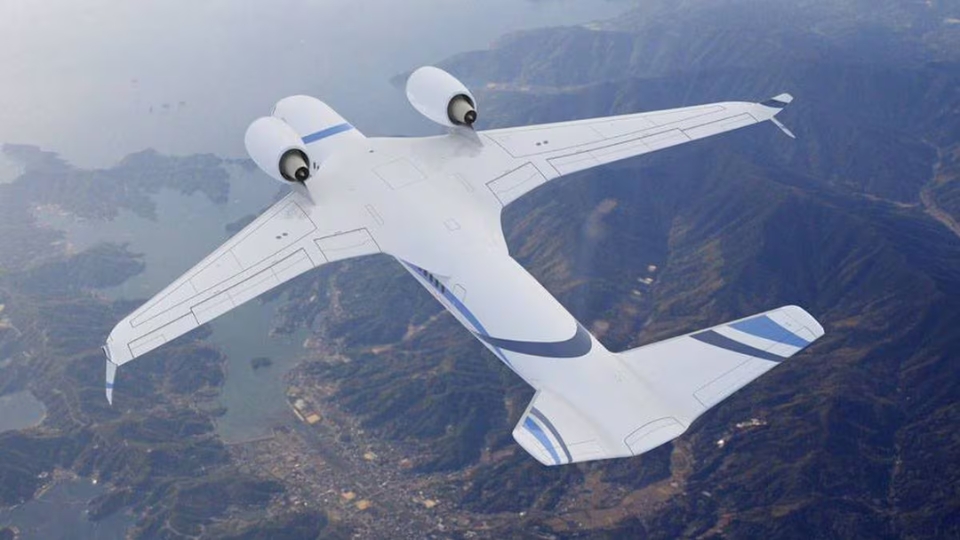
Manufacturers are also experimenting with blended wing body designs that merge the fuselage and wings into one aerodynamic structure. This design could revolutionize efficiency by significantly lowering drag and fuel burn.
As technology advances, each new aircraft generation becomes lighter, smarter, and cleaner, pushing aviation closer to carbon neutrality.
Adventure and Entertainment in Alaska
Wings of Alaska takes you on breathtaking journeys through the Alaskan wilderness, offering unforgettable experiences. After exploring the great outdoors, you can unwind with your favorite online casino. Both adventures and gaming provide excitement and memorable moments. Embrace the thrill of exploration in every way.
Conclusion
Aircraft design plays a key role in improving fuel efficiency. Engineers achieve this through aerodynamic precision, lightweight materials, and smarter systems. Every design decision—from wing shape to engine placement — helps reduce drag and optimize energy use.
As aviation moves into the future, sustainability and efficiency will remain central goals. The continued pursuit of innovation ensures that aircraft not only fly faster and farther but also protect the environment for generations to come.